Myelodysplastic Syndrome Explained: The Unexpected Symptoms Many People Overlook
Myelodysplastic syndrome is a complex blood disorder that often progresses quietly, with symptoms that are easy to dismiss or misinterpret. Fatigue, frequent infections, or unexplained bruising may appear long before a diagnosis is considered. Understanding these unexpected signs can help people recognize when routine issues may point to deeper problems within the bone marrow.
This blood disorder represents a group of conditions that fundamentally alter how bone marrow functions. When this vital tissue fails to produce adequate healthy blood cells, the resulting symptoms can be subtle yet persistent, often mimicking other common health conditions. Many individuals experience these changes gradually, making recognition particularly challenging for both patients and healthcare providers.
Unexpected Early Symptoms That People Commonly Overlook
The initial signs of this condition frequently masquerade as everyday health concerns. Persistent fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest often tops the list of overlooked symptoms. Unlike typical tiredness, this exhaustion feels overwhelming and interferes with daily activities. Frequent infections that seem to linger longer than usual may indicate compromised white blood cell function.
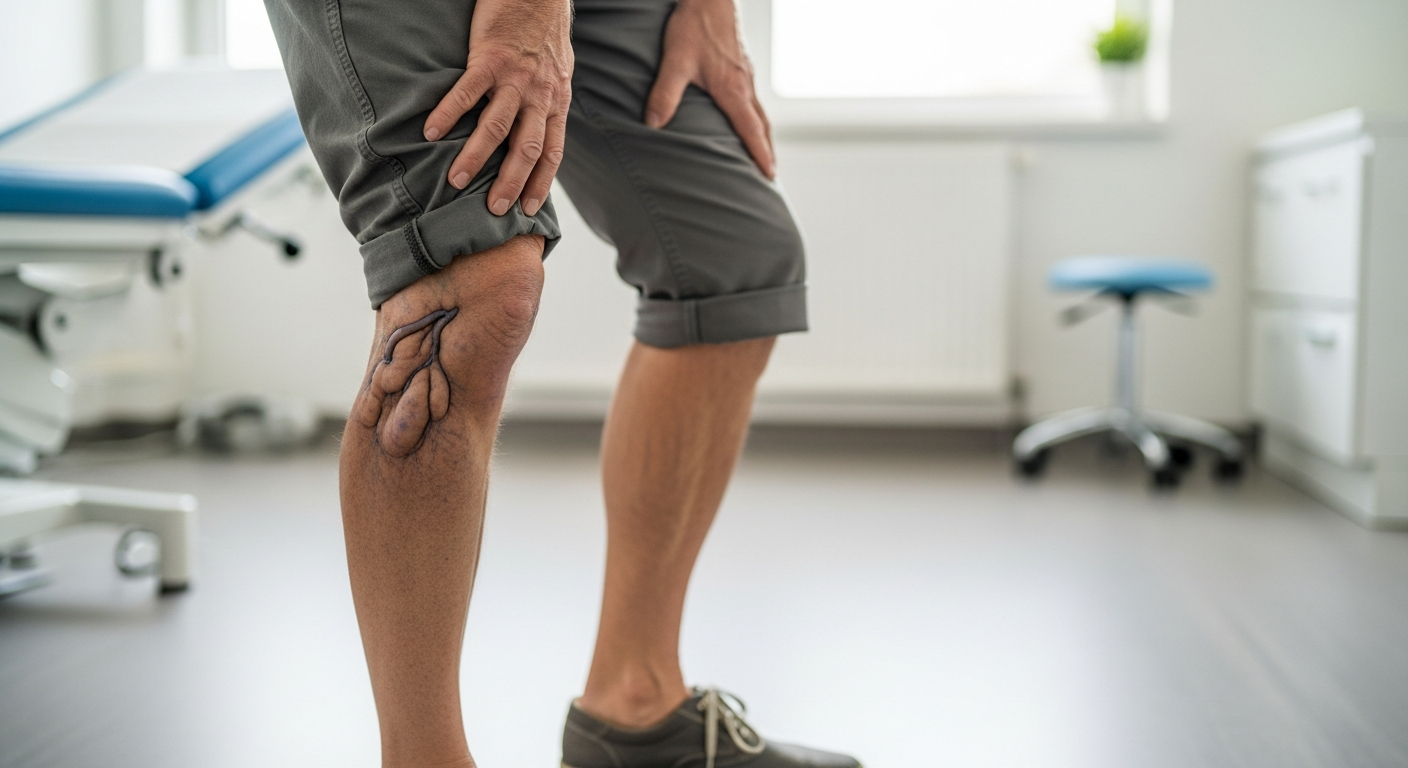
Unexplained bruising, particularly in areas not subject to obvious trauma, represents another commonly dismissed warning sign. Small red or purple spots on the skin, known as petechiae, may appear without apparent cause. Shortness of breath during routine activities that previously caused no difficulty can signal developing anemia. Additionally, pale skin, particularly noticeable in the nail beds and inner eyelids, often develops so gradually that it goes unnoticed.
Physical and Blood-Related Changes That May Appear Before Formal Diagnosis
Before laboratory tests reveal abnormal blood counts, physical manifestations often emerge. Dizziness or lightheadedness, especially when standing quickly, may indicate dropping red blood cell levels. Cold hands and feet, along with general sensitivity to temperature changes, frequently accompany developing anemia.
Bleeding tendencies become more apparent as platelet counts decline. This might manifest as prolonged bleeding from minor cuts, frequent nosebleeds, or heavier menstrual periods in women. Some individuals notice their gums bleeding more easily during routine dental care. Headaches may become more frequent or severe, potentially related to changes in blood cell counts and circulation.
Weight loss without dietary changes or increased physical activity sometimes occurs, though this symptom varies significantly among individuals. Bone pain, particularly in the ribs or sternum, may develop as the bone marrow struggles to function normally.
How This Condition Disrupts Normal Bone Marrow and Blood Cell Production
Healthy bone marrow continuously produces three essential types of blood cells: red blood cells for oxygen transport, white blood cells for immune defense, and platelets for blood clotting. This disorder interferes with this process at the cellular level, causing the bone marrow to produce abnormal, immature cells that cannot function properly.
These defective cells often die before entering the bloodstream, leading to low blood counts despite increased bone marrow activity. The condition creates a paradox where the bone marrow appears active under microscopic examination, yet circulating blood cell numbers remain inadequate. This dysfunction affects each cell type differently, explaining the varied symptom patterns individuals experience.
The genetic mutations underlying this disorder accumulate over time, progressively worsening bone marrow function. As healthy stem cells become increasingly rare, the body’s ability to maintain normal blood cell levels deteriorates, leading to more pronounced symptoms.
Risk Factors and Underlying Conditions Associated with Development
Age represents the most significant risk factor, with most cases occurring in individuals over 65. Previous cancer treatments, particularly chemotherapy and radiation therapy, substantially increase risk. Certain genetic disorders, including Down syndrome and Fanconi anemia, predispose individuals to developing this condition.
Exposure to specific chemicals, including benzene and certain pesticides, has been linked to increased risk. Smoking tobacco products doubles the likelihood of developing this disorder. Some inherited genetic mutations, though rare, significantly elevate risk levels.
Previous blood disorders, such as aplastic anemia or certain inherited bone marrow failure syndromes, may progress to this condition. Individuals with compromised immune systems, whether from medications or underlying conditions, face elevated risk levels.
When Ongoing Symptoms Suggest the Need for Further Medical Evaluation and Testing
Persistent fatigue lasting more than two weeks without obvious cause warrants medical attention, particularly when accompanied by other concerning symptoms. Frequent infections, especially those that resolve slowly or recur quickly, should prompt evaluation.
Unexplained bleeding or bruising, particularly when multiple symptoms occur simultaneously, requires professional assessment. Any combination of persistent fatigue, frequent infections, and unusual bleeding patterns should trigger immediate medical consultation.
Individuals over 60 experiencing these symptoms, especially those with previous cancer treatment history, should seek prompt evaluation. Blood tests can quickly reveal abnormal cell counts, though definitive diagnosis requires bone marrow examination.
Regular monitoring becomes crucial for individuals with known risk factors. Early detection significantly improves treatment options and outcomes, making awareness of these overlooked symptoms particularly valuable.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Recognizing the subtle signs of this blood disorder requires attention to persistent, unexplained changes in energy levels, infection patterns, and bleeding tendencies. While these symptoms may seem commonplace individually, their combination and persistence can signal underlying bone marrow dysfunction. Understanding these overlooked indicators empowers individuals to seek appropriate medical evaluation when necessary, potentially leading to earlier diagnosis and improved treatment outcomes.