How Driver Assistance Features Support Safety
In the evolving landscape of automotive technology, driver assistance features have become pivotal in enhancing road safety. As we move into 2025, these advanced systems are no longer luxury add-ons but essential components designed to reduce accidents, protect passengers, and improve overall driving experiences. This article explores how driver assistance features support safety, the technologies involved, and their impact on drivers and road users alike.

Understanding Driver Assistance Features
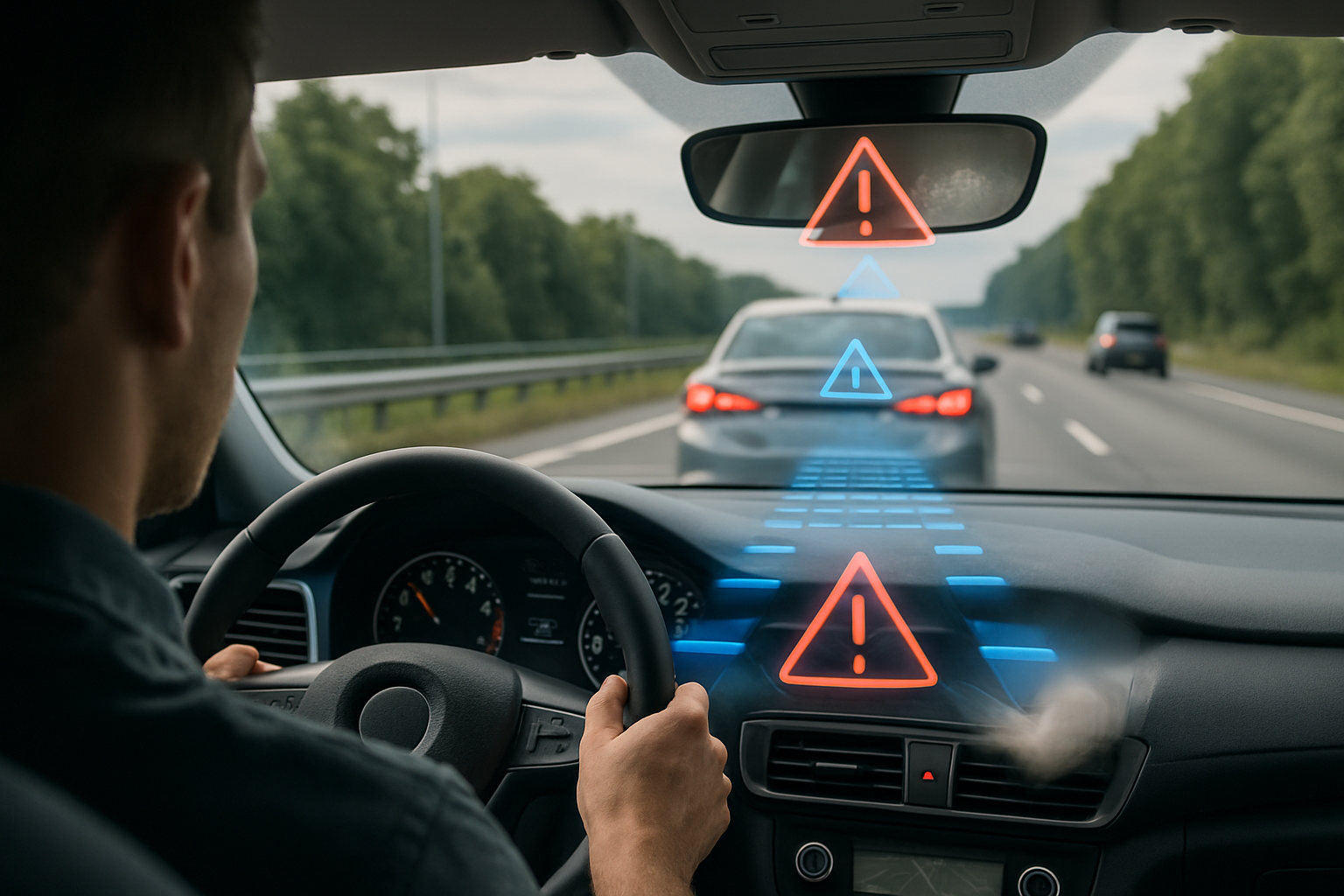
Driver assistance features, often referred to as Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), encompass a range of technologies aimed at helping drivers operate their vehicles more safely. These systems utilize sensors, cameras, radar, and artificial intelligence to monitor the vehicle’s surroundings and provide real-time feedback or automatic interventions.
Common examples include:
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): Maintains a safe distance from the vehicle ahead by adjusting speed automatically.
- Lane Keeping Assist (LKA): Helps prevent unintentional lane departure by gently steering the vehicle back into its lane.
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): Detects imminent collisions and applies brakes automatically if the driver doesn’t respond in time.
- Blind Spot Detection: Alerts drivers of vehicles in their blind spots during lane changes.
- Parking Assistance: Helps with parallel and perpendicular parking using sensors and cameras.
These features work collaboratively to mitigate human error, which remains the leading cause of traffic accidents worldwide.
Enhancing Safety Through Real-Time Monitoring and Intervention
One of the most significant ways driver assistance features support safety is through real-time monitoring and proactive intervention. Human drivers can be distracted, fatigued, or simply make mistakes—factors that contribute to a majority of road accidents. ADAS technologies act as a second pair of eyes and hands, continuously scanning the environment and aiding the driver.
Reducing Collision Risks
Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) is a prime example of how technology can prevent accidents. By using radar and camera data, AEB systems detect potential collisions with other vehicles, pedestrians, or obstacles. If the system senses an imminent impact and the driver does not respond promptly, it automatically applies the brakes, often reducing the severity of a crash or avoiding it altogether.
Similarly, Forward Collision Warning (FCW) systems alert drivers with audible and visual signals when they are closing in too fast on a vehicle ahead. These timely warnings give drivers a chance to react before a dangerous situation develops.
Preventing Lane Departure and Side Collisions
Lane Keeping Assist and Lane Departure Warning systems help maintain proper lane discipline, which is crucial on highways and busy roads. These systems monitor lane markings and gently steer the car back if it detects unintentional drifting. This reduces the risk of side collisions and road departures, which are common causes of serious accidents.
Blind Spot Detection systems use sensors to monitor areas that are difficult for drivers to see, especially during lane changes or merging. By alerting drivers to vehicles in their blind spot, these technologies help prevent side-swipe collisions.
Supporting Driver Awareness and Reducing Fatigue
Fatigue and inattention are major contributors to traffic accidents, especially during long drives or night-time travel. Driver assistance features play a vital role in supporting driver awareness and mitigating fatigue-related risks.
Driver Monitoring Systems
Some modern vehicles include driver monitoring systems that use cameras or sensors to track the driver’s eye movement, head position, and even grip on the steering wheel. If signs of drowsiness or distraction are detected, the system issues alerts encouraging the driver to take a break or refocus.
Adaptive Cruise Control and Traffic Jam Assist
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) reduces the mental load on drivers by maintaining a safe speed and distance without constant pedal input. When combined with Traffic Jam Assist, these features can take over acceleration, braking, and steering during slow-moving traffic, reducing stress and fatigue.
By automating routine driving tasks, these systems allow drivers to stay more relaxed and attentive, lowering the chance of accidents caused by tiredness or inattention.
The Road Ahead: Integration and Autonomous Driving
As we approach 2025, driver assistance features are becoming more integrated and sophisticated, paving the way toward fully autonomous vehicles. The continuous improvement of sensors, artificial intelligence, and connectivity will enhance the precision and reliability of safety systems.
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
Future driver assistance systems are expected to incorporate Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication, enabling cars to exchange information with other vehicles, infrastructure, and even pedestrians. This technology can provide early warnings about hazards beyond the driver’s line of sight, such as upcoming traffic jams, road conditions, or emergency vehicles.
Toward Full Autonomy
While fully self-driving cars are still in development, the incremental improvements in driver assistance features represent crucial steps toward autonomy. Each safety system introduced today builds the foundation for vehicles that can operate independently with minimal human intervention, drastically reducing accidents caused by human error.
Conclusion
Driver assistance features are transforming road safety by combining real-time monitoring, automatic intervention, and enhanced driver awareness. As of 2025, these technologies have proven their value in preventing collisions, reducing driver fatigue, and supporting safer driving practices. With ongoing advancements and greater integration, ADAS will continue to play a critical role in creating safer roads for everyone. Ultimately, the widespread adoption of these systems is a vital stride toward a future where accidents are significantly minimized, and driving becomes safer and more enjoyable for all.
Disclaimer: All content, including text, graphics, images and information, contained on or available through this web site is for general information purposes only. The information and materials contained in these pages and the terms, conditions and descriptions that appear, are subject to change without notice.